Linux 温习(九): IO 重定向与进程管道
- 陈大剩
- 2023-02-05 12:59:02
- 1636
I/O 重定向
基本知识介绍
什么是I/O?
I/O输入/输出(Input/Output)的简称,I 即为输入,常见的输入设备有键盘和鼠标。O为输出,常见的打印机等。
什么是I/O重定向
学过HTML都知道,重定向(Redirect)就是通过各种方法将各种网络请求重新定个方向转到其它位置,(如:网页重定向、域名的重定向、路由选择的变化也是对数据报文经由路径的一种重定向),I/O重定向是把标准的输入与输出到其他文件或者其他终端
例如 1:终端0输入消息到终端1那么此过程叫做重定向(将终端0上的 ‘Redirect’ 重定向到终端 1)
# 终端 0
> tty
/dev/pts/0
> echo 'Redirect' > /dev/pts/1
>
# 终端 1
[root@localhost ~]# tty
/dev/pts/1
[root@localhost ~]# Redirect
例如 2:将date输出的结果重定向到date.txt
> date > date.txt
> cat date.txt
Sun Apr 3 11:20:32 CST 2022
Linux 的标准输入与输出
在/proc虚拟机文件系统中,可以查看内核与进程的一些信息,其中有很多数字
> ls /proc/2191/fd -li
total 0
32321 lr-x------ 1 root root 64 Apr 3 10:13 0 -> /dev/null
32322 l-wx------ 1 root root 64 Apr 3 10:13 1 -> /dev/null
32323 l-wx------ 1 root root 64 Apr 3 10:13 2 -> /dev/null
32324 lrwx------ 1 root root 64 Apr 3 10:13 3 -> /dev/null
每一个进程在运行时都会打开一些文件,每一个文件都会有一个指定的数字标识,这个标识就交文字描述符。
上述的进程中有0、1、2、3的文件描述符,这也是绝大多数进程都有的。0 表示标准输入,可以理解为键盘输入;1 表示标准输出,输出到终端;2 表示标准错误,输出到终端;3 及以上为常规文件描述符;
1,2可理解为执行命令时输出的结果,包括失败和成功;这么说可能看不明白,演示几个例子就知道了
使用范例
范例 1:使用不存在的whomi命令,且将错误重定向到 error.txt 文件中 (错误不在输出)
> whomi
-bash: whomi: command not found
> whomi 2> error.txt
> cat error.txt
-bash: whomi: command not found
范例 2:将date输出的内容重定向到date.txt
> date 1> date.txt
> cat date.txt
Sun Apr 3 12:20:32 CST 2022
有同学可能会有疑问 > 就直接输出了吗? 为什么还要 1> 其实系统是默认有1的,不加默认就是1;
输出重定向
输出重定向分为正确输出和错误输出
正确输出:1> 、1>> 等价于>、>>,1可省略
错误输出:2>、2>>
其中>表示覆盖,>>表示追加
使用范例
范例 1:输出重定向(覆盖)
> date 1> date.txt
> cat date.txt
Sun Apr 3 14:45:34 CST 2022
范例 2:输出重定向(追加)
> date 1>> date.txt
> cat date.txt
Sun Apr 3 14:45:34 CST 2022
Sun Apr 3 14:46:18 CST 2022
范例 3:错误输出到重定向
> ls /home/linux
ls: cannot access /home/linux: No such file or directory
> ls /home/linux 2>error.txt
> cat error.txt
ls: cannot access /home/linux: No such file or directory
范例 4:正确结果与错误结果都输出到相同位置
> ll /home/ /home/linux &>list.txt
> cat list.txt
ls: cannot access /home/linux: No such file or directory
/home/:
total 200
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 58 Apr 3 14:46 date.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 57 Apr 3 14:48 error.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 57 Apr 3 14:49 list.txt
范例 5:正确结果保存到list.txt,错误结果丢到/dev/null
> ll /home/ /home/linux 1>list.txt 2>/dev/null
输入重定向
输入只有正确输入,且可以带结束符。(EOF、Ctrl+d)
恰好与输出相反:<、<<
使用范例
范例 1:使用grep命令过滤root,没有改变输入端,默认为键盘,接着把输入端重定向到/etc/passwd
> grep 'root'
linxu
root
root
> grep 'root' < /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
范例 2:使用at命令创建一个计划,从现在开始 1 分钟后创建用户 linux ,按组合件Ctrl+d结束。
> at now +1 min
at> useradd linux
at> <EOF>
重定向案例
案例 1:利用重定向建立多行文件,并用EOF结束
> cat >file03.txt <<EOF
11
22
33
EOF
> cat file03.txt
11
22
33
案例 2:多条命名输出重定向(两条以上命令需要加括号)
> ls;date &>/dev/null
date.txt error.txt file03.txt list.txt memcached package.xml redis root test.sh zip-1.20.0 zip-1.20.0.tgz
> ls &>/dev/null ;date &>/dev/null
> (ls;date) &>/dev/null
Subshell
Subshell 是指圆括号里的命令会在另外的进程中执行。当需要让一组命令在不同目录下执行时,采用这种方法可以不修改主脚本的目录。
请仔细看当前目录,一直处于home目录中,不加括号则返回到了root目录下。
> ls /root/
anaconda-ks.cfg install.sh package.xml
> (cd /root/; ls)
anaconda-ks.cfg install.sh package.xml
>
> cd /root/; ls
anaconda-ks.cfg install.sh package.xml
[root@localhost ~]#
如果不希望某些命令执行对当前Shell环境产生影响,请在Subshell中执行(加括号)。
进程管道
管道实际上头也是一种重定向,重定向字符控制输出到文件,管道控制输出到其他程序,其实是将结果传递给下一个程序调用。管道符为“|”
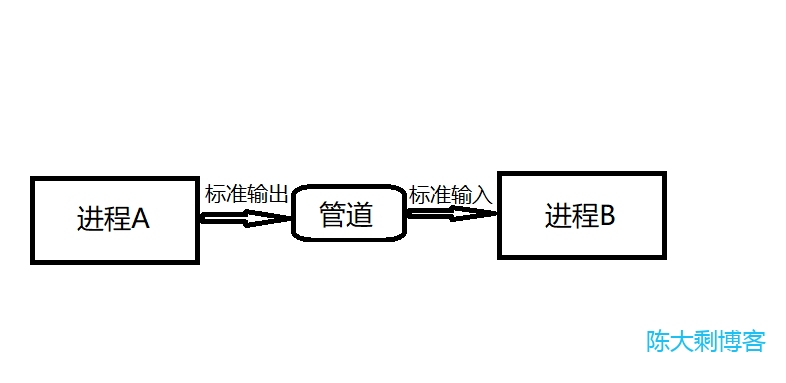
管道中有一种特殊的管道,tee 管道,如果我们既想把输出保存到文件中,又想在屏幕上看到输出内容,就可以使用tee管道,tee管道类似于生活中的三通水管。tee的作用是将一份标准输入多重定向,一份重定向到标准输出/dev/stdout,然后还将标准输入重定向到每个文件FILE中。
在使用管道时,前一个命令的标准错误不会被
tee读取
使用范例
范例 1: ps 命令结果通过管道给 grep 匹配
> ps -ef |grep php
root 1451 1 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: master process (/www/server/php/74/etc/php-fpm.conf)
www 1481 1451 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www
www 1482 1451 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www
www 1485 1451 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www
www 1490 1451 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www
www 1495 1451 0 10:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www
root 22436 3257 0 15:32 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto php
范例 2:查看系统是否有linux用户
> cat /etc/passwd |grep linux
>
范例 3:使用free命令显示系统内存使用信息,并使用tee命令将信息输出到屏幕,并保存到文件mem.txt中
> free -h | tee mem.txt
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 1.3G 99M 26M 375M 289M
Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
范例 4:使用 tee 捕获错误(无法捕获)
> ls /home/linux >list.txt 2>&1
> ls /home/linux 2>&1 | tee list.txt
ls: cannot access /home/linux: No such file or directory
范例 5:查看系统是否有root用户,将结果打印在屏幕和保存到文件中
> cat /etc/passwd |grep root | tee a.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
> cat a.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin